Vibe Coding a Todo App: From Zero to Deployed in One Session
How fast can you go from an empty folder to a fully deployed full-stack app? In this post, I'll walk through a live vibe coding session where I pair-programmed with an AI agent (Claude Code) to build a todo app using React for the frontend and Codehooks.io for the backend — all deployed to the cloud in minutes.
Every prompt I typed, every decision the agent made, and every line of code it wrote is documented here. Follow along and try it yourself.

The Setup
- Project:
vibetodo-eackon Codehooks.io (empty, freshly cleaned) - Stack: React + Vite (frontend), Codehooks.io (backend API + database + static hosting)
- Tool: Claude Code (AI coding agent in the terminal)
Install the Codehooks skill for Claude Code
Before starting, install the Codehooks Claude plugin so Claude Code understands the Codehooks platform, CLI, and APIs:
/plugin marketplace add RestDB/codehooks-claude-plugin
/plugin install codehooks@codehooks
Once installed, Claude Code auto-detects Codehooks projects and can deploy, query, and manage your backend directly from the conversation. Using a different AI coding agent? Check out our AI Agent Setup page for instructions on Cursor, Codex CLI, Windsurf, and more.
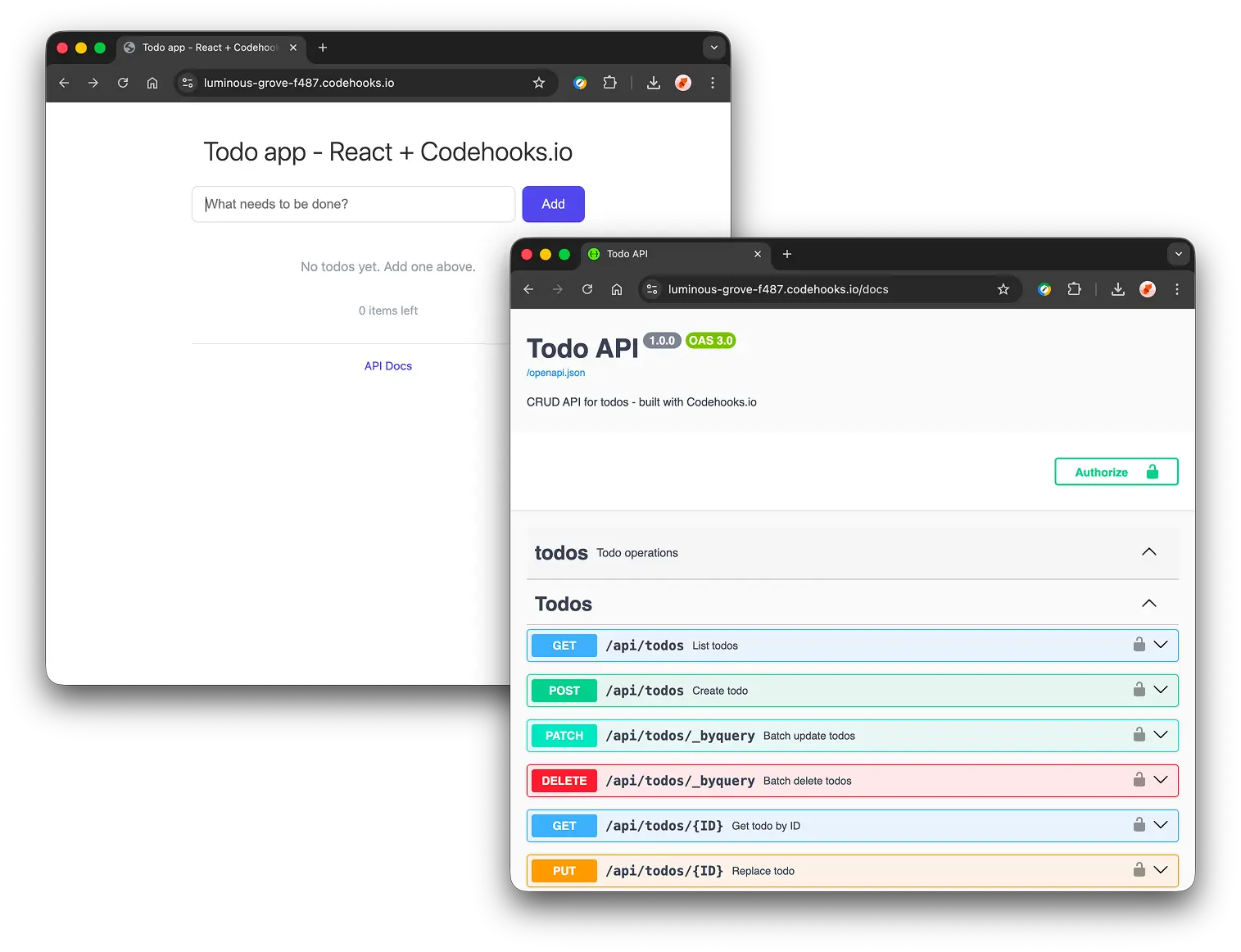
Screenshots of the final Todo app
A fully functional React todo app with a complete REST API, auto-generated Swagger documentation, and cloud deployment. All created in a single vibe coding session.
Prompt 1: The Kickoff
"Ok, in this session we'll vibe code the infamous todo app. We will use Codehooks for both frontend (React) and backend (CRUD API and database). The twist here is that we also will write about the process in a blogpost so other developers can read about and follow the dynamic process from zero to a finished deployed app. Document my prompts and your reasoning and actions in a blogpost.md file accordingly. Lets go, plan first, then code."
What happened: The Agent planned first
Before writing a single line of code, the agent entered plan mode — exploring the project state, reading the Codehooks API reference, and designing a 4-step approach:
- Initialize —
package.json+ start the blogpost - Backend — Zod schema +
crudlify()for instant CRUD API - Frontend — React SPA with Vite
- Deploy & verify — Build, deploy in ~5 seconds, test everything
The plan was approved. Let's execute.
Step 1: Project Initialization
The agent created package.json with all dependencies:
- Backend:
codehooks-js+zodfor validation - Frontend:
react,react-dom,vite,@vitejs/plugin-react
Both frontend and backend dependencies live in the same project — Codehooks handles the bundling and deployment.
Step 2: The Backend (12 lines of code)
Here's the entire backend — index.js:
import { app } from 'codehooks-js';
import { z } from 'zod';
const TodoSchema = z.object({
title: z.string().min(1).describe('Todo title'),
completed: z.boolean().default(false).describe('Completion status')
});
app.crudlify({ todos: TodoSchema }, { prefix: '/api' });
app.auth('/api/*', (req, res, next) => next());
app.auth('/*', (req, res, next) => next());
app.static({
route: '/',
directory: '/static',
default: 'index.html',
notFound: '/index.html'
});
export default app.init();
Agent reasoning
"The key decision here is using
crudlify()instead of writing manual routes. One line —app.crudlify({ todos: TodoSchema }, { prefix: '/api' })— auto-generates a complete REST API with Zod validation. That single line gives us:
GET /api/todos— list all todosPOST /api/todos— create a todo (validated against the Zod schema)GET /api/todos/:id— get one todoPUT /api/todos/:id— replace a todoPATCH /api/todos/:id— partial update (perfect for togglingcompleted)DELETE /api/todos/:id— remove a todoThe
app.static()block at the end serves the React SPA. ThenotFound: '/index.html'fallback enables client-side routing."
Step 3: The React Frontend
The agent created 4 files under frontend/:
frontend/vite.config.js — Vite config with a proxy to the live Codehooks API (for local dev) and build output to ../static:
import { defineConfig } from 'vite';
import react from '@vitejs/plugin-react';
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [react()],
server: {
proxy: { '/api': 'https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io' }
},
build: { outDir: '../static', emptyOutDir: true }
});
frontend/src/App.jsx — The todo app component. Key features:
- Add a todo via text input + form submit
- Toggle completed state with a checkbox (uses
PATCHto update just thecompletedfield) - Delete a todo with the X button
- Counter showing items remaining
- Clean, minimal inline styling — no CSS framework needed
Agent reasoning
"The frontend is intentionally simple. Each action (
addTodo,toggleTodo,deleteTodo) calls the Codehooks API and then re-fetches the list. This is the most straightforward pattern — no local state management needed beyond the form input. ThePATCHmethod is key: instead of sending the entire todo on toggle, we only send{ completed: !todo.completed }, whichcrudlifyhandles natively."
Step 4: Deploy and Verify
Three commands to go live:
npm install # Install dependencies
npx vite build frontend # Build React → /static
coho deploy # Deploy to Codehooks (~5 seconds)
Output:
Deployed Codehook successfully!
Testing the API with curl
Create:
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"title":"Buy milk","completed":false}' \
https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io/api/todos
{"title":"Buy milk","completed":false,"_id":"698cf5b86c156a91bb44f2ba"}
List:
curl https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io/api/todos
[{"title":"Buy milk","completed":false,"_id":"698cf5b86c156a91bb44f2ba"},
{"title":"Write blogpost","completed":false,"_id":"698cf5ba6c156a91bb44f2bc"}]
Toggle completed (PATCH):
curl -X PATCH -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"completed":true}' \
https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io/api/todos/698cf5b86c156a91bb44f2ba
{"title":"Buy milk","completed":true,"_id":"698cf5b86c156a91bb44f2ba"}
Validation (empty title rejected):
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"title":""}' \
https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io/api/todos
[{"origin":"string","code":"too_small","minimum":1,"inclusive":true,
"path":["title"],"message":"Too small: expected string to have >=1 characters"}]
All tests passed. The React SPA loads at the base URL and is fully functional.
The Result
Live app: https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io/
From zero to deployed: under 5 minutes
Let that sink in. From the moment I typed the kickoff prompt to a fully deployed, tested full-stack app live on the internet — under 5 minutes. Here's the breakdown:
| Phase | Time |
|---|---|
| Planning (agent explores + designs approach) | ~30 seconds |
Backend code generation (index.js) | ~10 seconds |
| Frontend code generation (4 files) | ~15 seconds |
npm install | ~9 seconds |
vite build | ~0.4 seconds |
coho deploy | ~5 seconds |
| API testing (6 curl commands) | ~15 seconds |
| Total wall time | ~90 seconds |
The rest of the time was the agent writing this blogpost. The actual app was live before the ink was dry on Step 2 of the documentation.
This is the power of vibe coding with the right stack: you describe what you want, the agent figures out how, and the platform handles the where.
What we built
- A full-stack todo app with React frontend and Codehooks backend
- Zod-validated CRUD API auto-generated from a schema
- 6 REST endpoints from a single line of code
- Frontend and backend deployed together to the same URL
File count
| File | Lines | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
index.js | 24 | Backend: schema + API + static serving |
frontend/src/App.jsx | 120 | React todo app component |
frontend/src/main.jsx | 8 | React entry point |
frontend/vite.config.js | 14 | Build config + dev proxy |
frontend/index.html | 12 | HTML shell |
package.json | 20 | Dependencies |
| Total | ~200 |
Prompt 2: "Add OpenAPI docs and Swagger"
"And finally lets add openapi docs and swagger."
One more app.openapi() call — that's it. Since we used crudlify() with a Zod schema, Codehooks auto-generates the full OpenAPI 3.0 spec from the schema. No manual route documentation needed.
app.openapi({
info: { title: 'Todo API', version: '1.0.0', description: 'CRUD API for todos - built with Codehooks.io' },
tags: [{ name: 'todos', description: 'Todo operations' }]
});
One coho deploy later:
- Swagger UI: https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io/docs
- OpenAPI spec: https://luminous-grove-f487.codehooks.io/openapi.json
All 6 CRUD endpoints are fully documented with schemas, parameters, and response types — generated automatically from the Zod TodoSchema. Zero extra work.
Prompt 3: "Add a cron job that empties the todos collection every hour"
"Add a cron job that empties the todos collection every hour"
Since this is a public demo app, we want to keep the database clean. Codehooks has built-in cron job support via app.job(). Two lines:
app.job('0 * * * *', async () => {
const conn = await Datastore.open();
await conn.removeMany('todos', {});
console.log('Cron: cleared todos collection');
});
The cron expression 0 * * * * fires at minute 0 of every hour. removeMany with an empty query {} wipes the entire collection. Deployed with one coho deploy — the job is now scheduled automatically by the platform.
The vibe coding takeaway
The entire session — from empty folder to deployed, tested app — took one conversation. The agent planned before coding, made decisions transparent, and tested everything before declaring success.
The key enablers:
- Codehooks
crudlify()— turned a Zod schema into a full REST API in one line - Codehooks
app.static()— served the React SPA from the same deployment - Vite — fast builds with zero config
- AI agent — handled the boilerplate so we could focus on the architecture
No Docker. No CI/CD pipeline. No infrastructure config. Just code and deploy.
